While most people think of a microscope as the compound model in lab classes, this is just one type of microscope. While all microscopes are used to enlarge small objects, some are more powerful than others. The least powerful are ideal for kids, while the most powerful are used by forensic science technicians, jewelers, medical technicians, and researchers. The type of microscope they use depends on their unique needs, samples, and resources. Their prices range from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
What Are The Types Of Microscopes And Their Uses?
There are many different types of microscopes, and they all solve different problems. Below are six types of microscopes and their applications.
6 Categories Of Microscopes
- Stereo Microscope
- Simple Microscope
- Inverted Microscope
- Compound Microscope
- Polarizing Microscope
- Metallurgical Microscope
Stereo Microscopes
Stereo microscopes are useful when looking at samples that you can hold with your hand. The microscope offers magnification between 10x to 40x and will give a 3D dimension of the sample. Stereo microscopes also offer both reflected and transmitted illuminations. You can use them to view samples that don’t allow light to pass through them. These microscopes are used in quality control, manufacturing, science, school dissection projects, botany, and coin collecting. Some of the samples you can view include flowers, frog anatomy, wires, metal and plastic parts, coins, fabric weaves, and insects.
Simple Microscopes
Simple microscopes were the first microscopes to be invented in the seventeenth century by scientist Antony Van Leeuwenhoek. He integrated a holder and convex lens for specimens. Simple microscopes offered a 200x to 300x magnification. They were powerful enough to offer Van biological specimen information such as different shapes of red blood cells and the nature of other biological materials.
Simple microscopes are rarely used nowadays as the second lens introduction increased the magnification power and led to more powerful microscope compounds.
Inverted Microscopes
There are two types of inverted microscopes: inverted metallurgical microscopes and inverted biological microscopes.
Inverted metallurgical microscopes are often used in metallurgical research to observe large objects using high magnification to find fractures and faults in metal surfaces and objects. The polished and smooth samples, known as pucks, are placed on the stage and viewed through a beneath housed objective lens.
On the other hand, inverted biological microscopes offer 40x, 100x, and even 200x or 400x magnification. Using beneath housed objective lenses, you can use the microscope to observe living samples on a flat stage in a Petri dish. Biological inverted microscopes are used in the research industry to study and analyze cells, tissues, and other living cells. The microscope is also useful in living cell imaging, in-vitro fertilization, neuroscience, microbiology, and developmental and cell biology.
Compound Microscopes
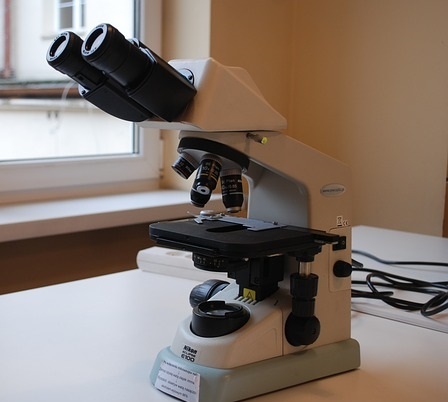
Also known as biological microscopes, compound microscopes employ multiple objective and single eyepieces on a rotating ring that allows switching to enhance magnification power. Compound microscopes are often used in high schools, laboratories, veterinary offices, pathology and histology, and wastewater treatment plants.
You place the sample to be viewed on a microscope slide with a cover slide to keep the sample in place and flatten it. Students often use prepared slides with samples embedded permanently between the layers to save time.
A compound microscope is used to view samples such as blood cells, tissues, cheek cells, bacteria, thin sections of organs, parasites, and algae. The samples viewed with a compound microscope are invisible to the naked eye. Compound microscope magnification is often 40x, 100x, 400x and sometimes 1000x.
Polarizing Microscopes
Polarizing microscopes use reflected and transmitted illumination and polarized light to examine rocks, chemicals, and minerals. The microscopes are often used by chemists, geologists, the pharmaceutical industry, and pathologists.
Polarizing microscopes have an analyzer and a polarizer. The analyzer resolves the amount and direction of light to illuminate a sample while the polarizer allows certain light waves to pass through the microscope. Polarizer mainly focuses on the different light wavelengths on a single plane, and this helps the microscope perfectly view birefringent materials.
Metallurgical Microscopes
Metallurgical microscopes are high-powered and designed to view opaque samples. Reflected light illuminates the samples through the objective lenses offering 50x, 100x, 200x, and even 500x magnification. This lets observers discover micron-level cracks in paints and metals and grain sizing.
Metallurgical microscopes are often used in automobile manufacturing, aerospace, and other companies dealing with crystals, ceramics, glass, polymers, and composites.
Frequently Asked Questions
What microscope is used to view viruses?
The most effective microscope used to view viruses is the transmission electron microscope. TEM has contributed greatly to virology, including diagnosing different viral infections, discovering varied viruses, and investigating host cell-virus interactions.
What type of microscope is used in microbiology?
A fluorescence microscope is often used in clinical microbiology. The microscope is used to identify pathogens, find the location of certain cell structures and molecules and find certain species in an environment.
What is an inverted microscope used for?
An inverted microscope is used in observing living organisms and cells at the bottom of a big container like tissues culture flask in a more natural condition.
Can red blood cells be seen with a light microscope?
Yes. The light microscope has a short field depth at high resolution, which effectively observes red blood cells.
Can electron microscopes see bacteria?
Electron microscopes offer helpful information on the size, localization, and shape of single bacteria within the biofilm steps formation process, production of EPSs, and bacterial interaction.
What type of microscope is used to view protozoa?
The best type of microscope used to observe protozoa is the compound microscope with power magnification of 10x, 40x, and 400x.
What microscope has an opaque disc?
The dark field microscope. These microscopes are used to illuminate and view unstained samples.
What is the difference between inverted and upright?
The objectives of an inverted microscope are below the stage where you place the samples, while the objectives of an upright microscope are above the stage where you place the samples.
